Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI)
Hip Anatomy
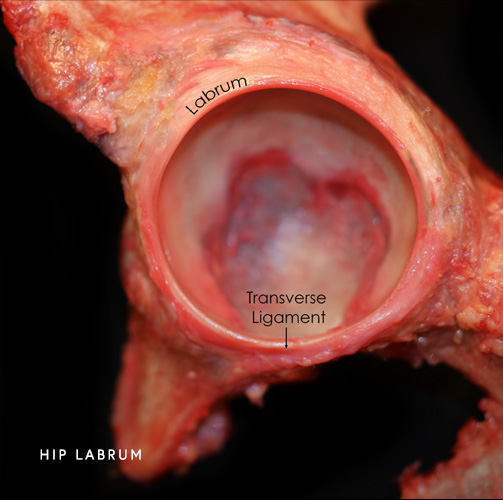
The hip is a ball and socket joint. The socket is the part of the hip bone called the acetabulum, and the head of the femur is the ball. Articular cartilage covers both the ball and the socket and functions to reduce friction for smooth joint movement. The labrum is ring of very strong fibrocartilage (like a rubberband) that lines the outer edge of the socket and deepens the hip socket.
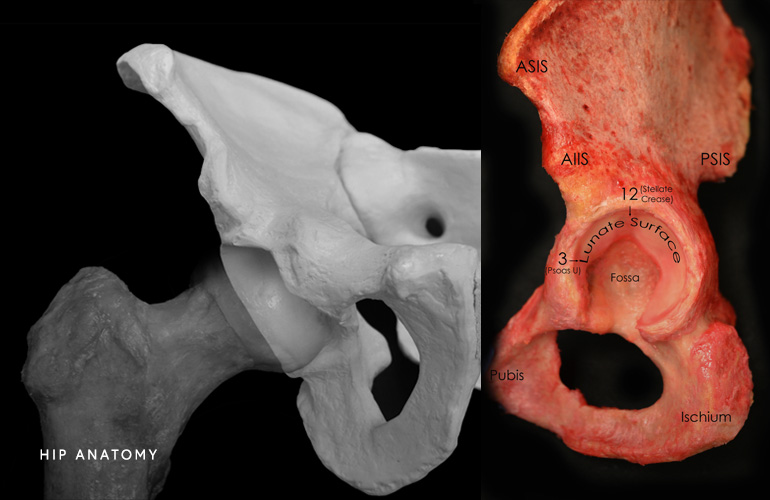
The labrum plays an important role in maintaining normal hip function. It functions to tighten the seal between the bones for joint stability, allows for a wide range of motion and helps to maintain the alignment between the bones. In a normal, healthy joint the ball fits tightly to the acetabulum. When the bones are abnormally shaped, they can rub against each other and damage the joint.
What is FAI?
FAI (femoroacetabular impingement) is hip impingement caused by a structural problem, specifically bony abnormalities that lead to abnormal contact between the acetabulum and the femoral head. The abnormality may be a developmental deformity or acquired (caused by injury or repetitive movements). Hip deformities and the abnormal growth of bone on the ball and/or the socket alter normal biomechanics and lead to hip instability, labrum injury, and accelerated joint degeneration. FAI is a common cause of hip and groin pain in young, active patients.
The location of the impingement can be described as either the CAM type or Pincer-type or both. CAM type is caused by the abnormal shape of the femoral head and neck, while the Pincer-type is caused an abnormal shape of the acetabulum. Repeated microtrauma causes bone spurs, damage to the labrum, hip joint degeneration and osteoarthritis.
What are the symptoms of FAI and a labral tear?
Most labral tears are due to FAI, and the symptoms usually overlap. A labral tear does not usually heal on its own because it has a limited blood supply. Some people live active lives and never have problems. Symptoms indicate damage to the cartilage or labrum. Common symptoms of FAI include:
- Intermittent deep groin pain or ache (most common)
- Pain at the outside of the joint
- Sharp stabbing pain when twisting, turning or squatting as when getting in or out of a car or a chair
- A dull ache from prolonged sitting or walking
- A clicking or locking sound when the hip is moved
- Instability and decreased range of motion
- Stiffness and limping
How is FAI diagnosed?
During your consultation with Dr. Jorge Chahla, a Chicago sports medicine surgeon, he will review your medical history, symptoms, past injuries and the movements that cause your hip pain. He will conduct a physical examination checking range of motion including flexion, adduction, and rotation to diagnose your impingement. A cortisone injection can help to confirm the diagnosis. If the pain goes away, it confirms that the source of the pain is due to FAI.
Imaging tests are necessary to definitively diagnose your condition. X-rays will reveal abnormally shaped bones, and an MRI will reveal damage to the soft tissue such as the labrum (a labral tear). A CT scan is usually not necessary, but in some cases Dr. Chahla may order one. A CT scan will provide details about the shape of the bones and the location of abnormal bone as well as to determine the rotation of the bones.
Can hip impingement cause buttocks pain?
Yes. Pain can be felt in the front of the thigh or down the buttocks. It FAI can also cause low back pain, and sharp pain when getting into or out of a car or a chair.
What causes FAI?
Many people have a misshapen hip joint that may not cause problems until it is overused and pushed beyond the hip’s normal range of activity. It is often misdiagnosed as hip bursitis, hip muscle strain, injury due to trauma to the hip joint, or hip dislocations.
What is the hip impingement test?
This is a test that Dr. Chahla will use when he examines you. He will ask you to bring your knee to your chest and then rotate it in toward the opposite shoulder (FADIR [flexion adduction and internal rotation]). If this causes pain, it is positive for FAI. However, imaging tests will be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. A comprehensive physical exam is key to determine the cause of your hip pain.
Does a hip impingement need surgery?
Some people live active lives, never knowing they have FAI, and don’t have any problems. By the time symptoms develop there is usually some damage to the hip cartilage (labrum) and with repeated use, the damage will progress. The reason athletes are often diagnosed with FAI is because they overuse the joint in extreme ranges of motion which damages the labrum and causes pain.
In mild to moderate cases, FAI symptoms can improve with nonsurgical treatment. This involves a change in activities to avoid movements that cause pain, including taking time off from athletics, using over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation, and physical therapy. Symptoms should resolve within several weeks. Corticosteroid injections can also help relieve pain. Chiropractic treatments can sometimes aggravate the condition.
When is FAI surgery indicated?
When nonsurgical treatments do not relieve pain and imaging reveals severe tears or detachment of the labrum, or damage to the articular cartilage, surgery will be recommended. FAI surgery can be performed in a minimally invasive procedure called hip arthroscopy, which is usually an outpatient procedure. However, in some cases open surgery may be required. Hip surgery is customized for each patient because each patient’s anatomy and condition are different.
How long does it take to recovery from hip surgery for FAI?
Most people can recover full, unrestricted activity in 4-6 months with a good physical therapy program.
What is hip preservation?
Hip preservation refers to the use of procedures to protect and maintain the labrum (the cartilage that lines the hip bone to deepen the hip socket) to prolong the natural lifespan of the hip, prevent arthritis of the joint, and to avoid or delay hip replacement surgery. FAI predisposes to premature joint degeneration. Hip replacement surgery is the treatment for advanced arthritis of the hip.
Orthopedic surgeon Dr. Jorge Chahla is a sports medicine surgeon in Chicago, Illinois who specializes in the treatment of hip injuries. He in internationally recognized for his contributions to the field of sports medicine and is a pioneer in novel therapies. Dr. Chahla’s focus is on customized and personalized care to meet the needs of each of his patients. He uses minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures to preserve the natural joint and reduce recovery time to accelerate his patients’ return to the activities they love.
At a Glance
Dr. Jorge Chahla
- Triple fellowship-trained sports medicine surgeon
- Performs over 500 surgeries per year
- Assistant professor of orthopedic surgery at Rush University
- Learn more



